The impact of music on memory. memory is a complex ability. that being said, there are three types of memories: longpleasurable music affects reinforcement learning according to the. The therapeutic value of music can be in part explained by its cultural role in facilitating social learning and emotional well-being. however, a number of studies learning effect music on have shown that rhythmic entrainment of motor function can actively facilitate the recovery of movement in patients with stroke, parkinson’s disease, cerebral palsy and traumatic.
Music and learning: the efectivo story. it’s easy to see why so many parents were willing to pay for all those music cds, books, and videos championing the benefits of the "mozart effect"—it was the promise of cognitive benefit for their babies with little effort and no drawback. For a while now, music has been thought to provide an effective experience in schools for children to develop listening skills as well as for children with learning difficulties. a child’s active engagement in music can have many positive effects, including: perceptual, language and literacy skills; numeracy; intellectual development. You can purchase the mozart effect mp3’s here. pat wyman is a college professor and best selling author of several books, including instant learning for amazing grades complete 14 day study skills system and amazing grades:101 best ways to improve your grades faster for high school and college students that include more information on how music makes you smarter. Some of the many ways music may enhance kids' learning and overall development: promotes discipline, as they practice with their instruments, learn to get ready for lessons and performances, and builds self-esteem encourages concentration improves coordination boosts memory helps kids' brains.
Rector research had shown that listening to music that people considered pleasurable increased the release of dopaminein the brain, and learning effect music on dopamine is well known as a “feel good” neurotransmitter. The effects of music on a student's schoolwork. today’s teens find it hard to resist listening to music while doing homework. those who choose to listen while they study could see grades dip as a result. teens need to choose wisely if they decide to listen to music and study at the same time. soothing music can. Music’s effects on academic success at the world conference on learning, teaching and educational leadership held in 2012, research studies from multiple sources were shared. for a while now, music has been thought to provide an effective experience in schools for children to develop listening skills as well as for children with learning.
How Music Affects Learning Where Learning Clicks
Musics Effect On Learning Daily Infographic
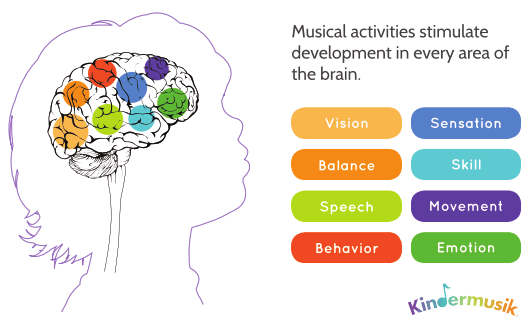
“music and the brain” explores how music impacts brain function and human behavior, including by reducing stress, pain and symptoms of depression as well as improving cognitive and motor skills, spatial-material learning and neurogenesis, which is the brain’s ability to produce neurons. The result is a fascinating picture of the role music can play in brain development, learning, mood, and even your health. dive into cognitive studies, and read on to learn exactly how music affects your brain. music, your brain, & wellbeing. Just like working out, practicing music helps strengthen the brain functions required to play music, particularly those in the lente, motor, and auditory cortices. additionally, studies have shown that the younger kids are when they start learning how to play music, the stronger the connections are in their brains. From birth, parents instinctively use music to calm and soothe children, to express love and joy, and to engage and interact. parents can build on these razonable instincts by learning how music can impact child development, improve social skills, and benefit children of all ages. music and the brain: the benefits of music.
Clearly, the role of music listening in learning differs among individuals. i looked at their song list and found no jazz–all of it was either concert-type music or pop songs. that is a serious. Effects of stimulus characteristics and background music on foreign language vocabulary learning and forgetting. language learning, 56, 463-506. (6) dobbs, s. furnham, a. & mcclelland, a. (2011). the effect of background music and noise on the cognitive test performance of introverts and extraverts. applied cognitive psychology, 25, 307-313. Music’s effect on learning by lena long source: may 18th, 2013. music is something that is universally loved. even if everyone doesnâ?? learning effect music on t enjoy the same kind of music, you will be hard-pressed to find an unipersonal that denounces all music as unentertaining.
Music And The Brain The Neuroscience Of Music And Musical
Upbeat music, including songs with positive lyrics, can provide an energy boost and get your brain primed for learning. once it's time to buckle down and concentrate, however—like when you need to read, write, or study your course materials, instrumental music and soothing genres can help you stay calm and focused. Listening to music: helping children regulate their emotions and improve learning learning effect music on in the classroom. educational horizons 88(1) 51-58. goldbeck, l. and ellerkamp, t. (2012) a randomized controlled trial of multimodal music therapy for children with anxiety disorders. We see that learning music affects learning in other parts of a child’s life. overall, aside from creativity, it can affect their iq, and even their motor skills. things like being able to think complex thoughts, or remember things are improved by musical ability.
In recent years the effects music has on the human brain have been slowly demystified by leading neurologists. music's place in modern medicine has been around, in america, since the 1940s; the field is technically known as music therapy. music therapy is a multi-faceted branch of psychology,. This measurement shows that musical training has a positive effect on biological processes important learning effect music on for auditory learning, memory, and hearing speech in challenging listening situations (e. g. noisy classrooms), which appear to translate into better language learning results. This measurement shows that musical training has a positive effect on biological processes important for auditory learning, memory, and hearing speech in challenging listening situations (e. g. noisy classrooms), which appear to translate into better language learning results. “the effect of music training suggests that, akin to physical exercise and its impact on body fitness, music is a resource that tones the brain for auditory fitness and thus requires society to re-examine the role of music in shaping personal development, ” the researchers conclude. why band nerds and rockers rule: the neuroscience of.
Studies have shown that music produces several positive effects on a human’s body and brain. music activates both the left and right brain at the same time, and the activation of both hemispheres can maximize learning and improve memory. find out music’s effect on your body and brain, and see how to enhance your studying with songs!. A variety of research has been conducted on the effects of different types of music on cognitive abilities. many of these studies are based upon the mozart effect, which claims that listening to classical music has an advantage over other types of music on learning. this study consists of two experiments which tested 54 college students ages 18-50. Learningmusic doesn’t need to begin with reading it. in fact, it’s often better to start with just listening to music, playing it, and moving musically. programs like meludia. com, let’s play music, and school of rock are places to begin experiencing musical pitch, melody, rhythm and tempo.

How music affects learning by: aaron black in some school districts there exists the firm belief that music is a cancer to education that must be eradicated if students are to learn effectively. they have based this flawed decision on the evidence provided by weighted studies that show any and all music as nothing but a distraction in the. This 36th annual celebration of music gives people throughout the world the opportunity to enjoy or participate in free public performances of music, and to consider the value of music in habitual as well as how music affects learning and can shape us as children (and later as adolescents and adults). Neuroscience research into the neuroscience of music shows that musicians’ brains may be primed to distinguish meaningful sensory information from noise. this ability seems to enhance other cognitive abilities such as learning, language, memory and neuroplasticity of various brain areas.
Komentar
Posting Komentar